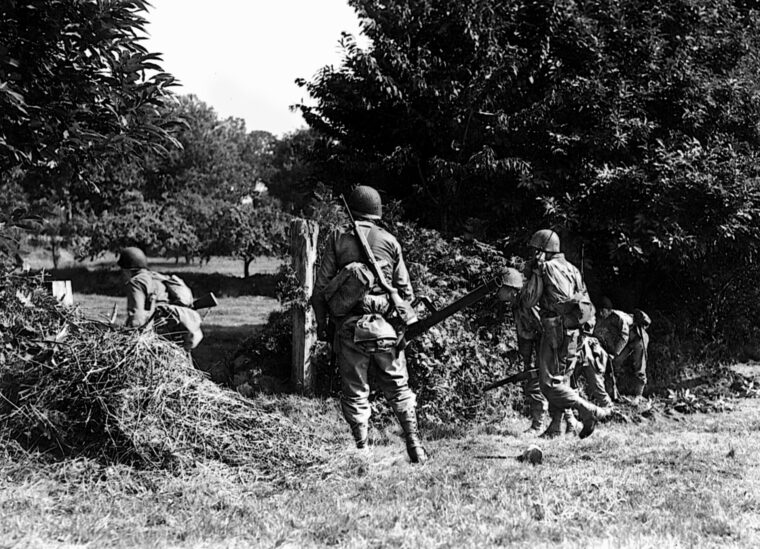

D-Day
The 12th Army Group Gets Going
By Steve Ossad
A few months after the Normandy campaign and with other fronts competing for the American public’s attention, Lt. Read more

Code named Operation Overlord, the D-Day Invasion occurred on June 6, 1944, as elements of five Allied infantry and three Allied airborne divisions assaulted the Normandy coast of Nazi-occupied France during World War II. Under the overall command of General Dwight D. Eisenhower, the landings on Gold, Juno, Sword, Utah, and Omaha beaches succeeded in establishing a foothold on the continent. Following an arduous campaign in Normandy and savage fighting across the German frontier, troops of the Western Allies met the Soviet Red Army, advancing from the East, and Nazi Germany surrendered on May 7, 1945.

D-Day
By Steve Ossad
A few months after the Normandy campaign and with other fronts competing for the American public’s attention, Lt. Read more
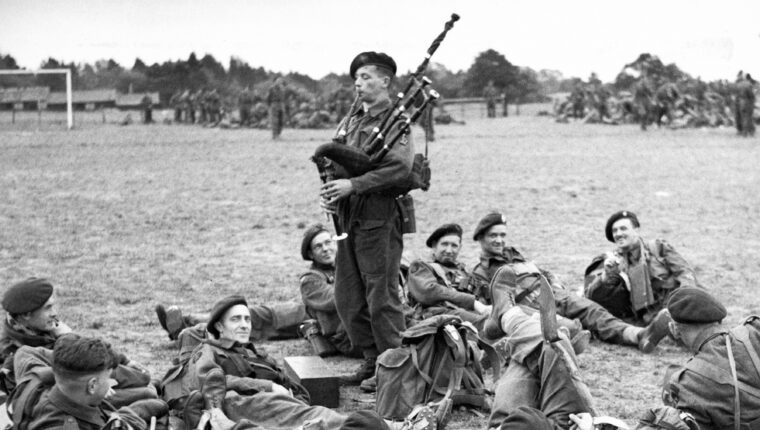

D-Day
The image of the Scottish piper standing erect under fire was commemorated in the film The Longest Day nearly two decades after the D-Day landings of June 6, 1944. Read more
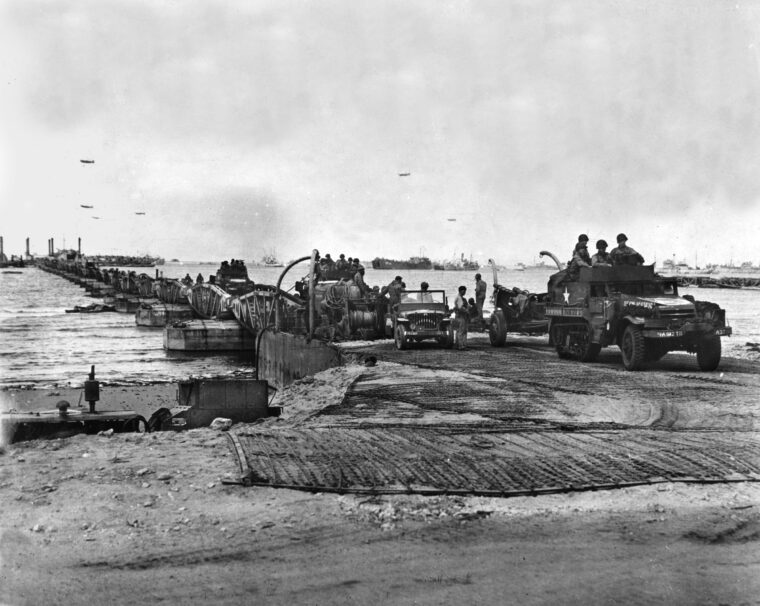

D-Day
No Allied amphibious invasion in World War II left such a bitter legacy as Operation Jubilee, the ill-fated British-Canadian raid on the northern French port of Dieppe on Wednesday, August 19, 1942. Read more

D-Day
“Why the hell am I here?” Lt. Richard Winters asked himself as he pulled out of his parachute harness in the first hours of D-Day. Read more
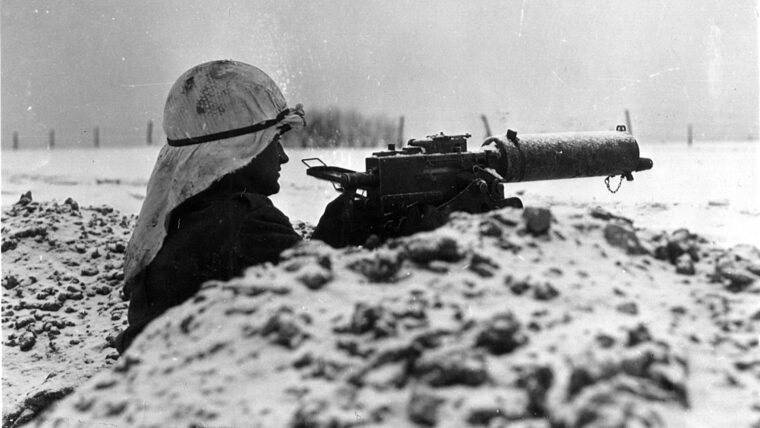

D-Day
Many people who never knew John Hanlon personally may remember him as that paratrooper who took the sheets back to Bastogne. Read more

D-Day
After sundown on July 17, something happened at a small port town 40 miles northeast of San Francisco that has never been fully explained…
The 7,500-ton Liberty ship SS E.A. Read more
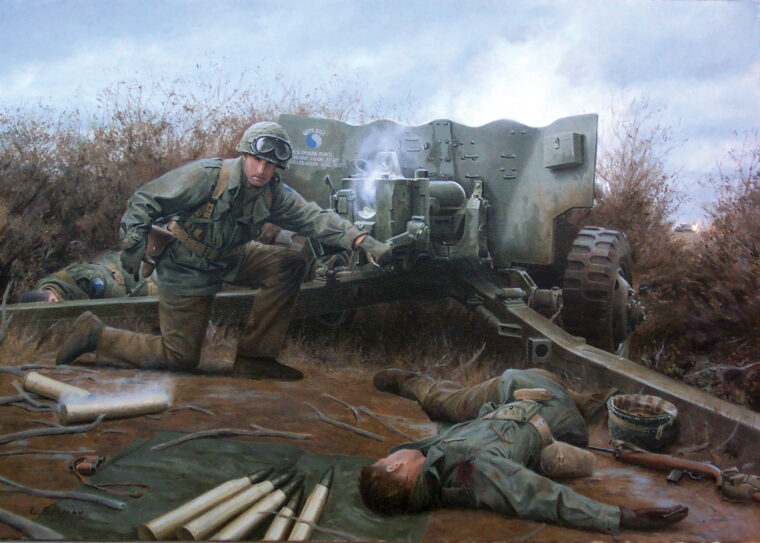

D-Day
Not all of the 68 infantry divisions available to the U.S. Army during World War II were made up of draftees and enlistees. Read more

D-Day
In 1934 the British War office accepted a new aircraft design eventually designated the Hawker Hurricane Mark 1. Read more
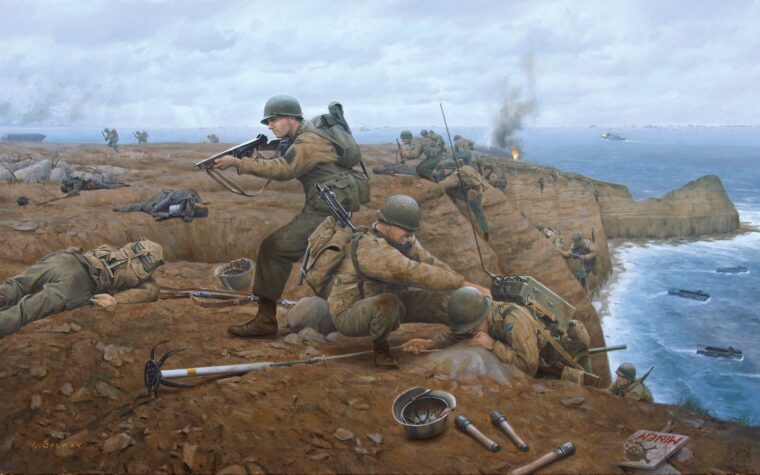

D-Day
On the morning of June 6, 1944, the 2nd Ranger Battalion, commanded by Lt. Col. James Earl Rudder, began its ascent of a sheer 100-foot precipice called Pointe du Hoc. Read more

D-Day
Behind the strategy that governed the American air war in Europe during World War II lay events and ideas that dated back to World War I and the 1920s. Read more
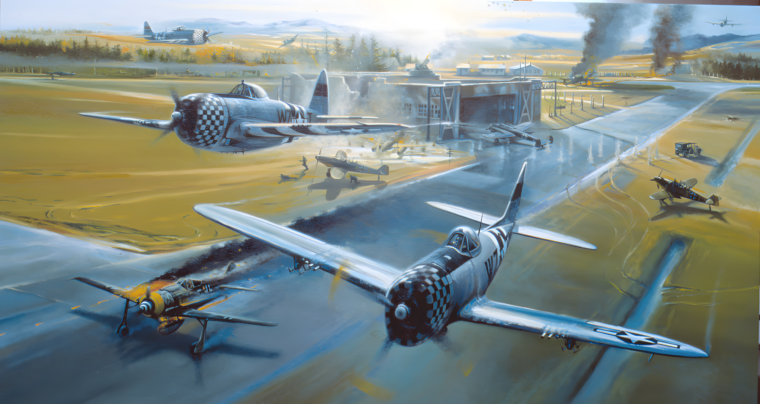

D-Day
The captured German pilot was cocky and boastful. He had just parachuted into the American airfield, now lit up by the fires of burning Republic P-47 Thunderbolts, a sprinkling of bright torches amid the gray January gloom and the dirty white snow. Read more
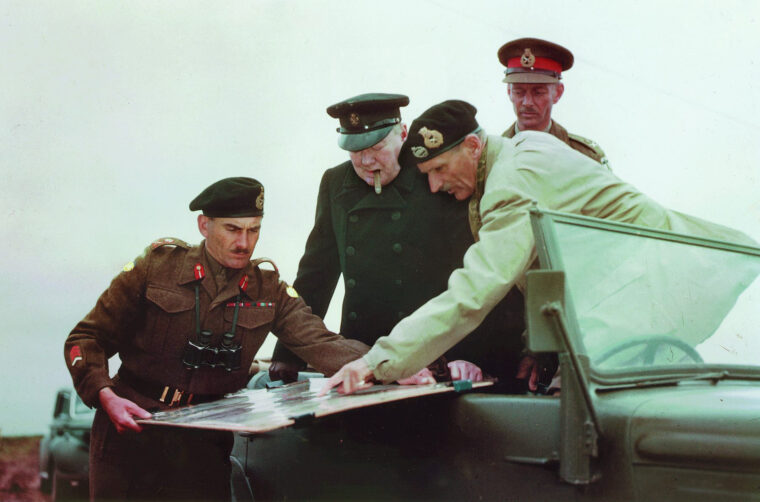

D-Day
In an August 14, 1944, General Bernard L. Montgomery was facing a manpower crisis, unable to drive the Germans out of Caen. Read more
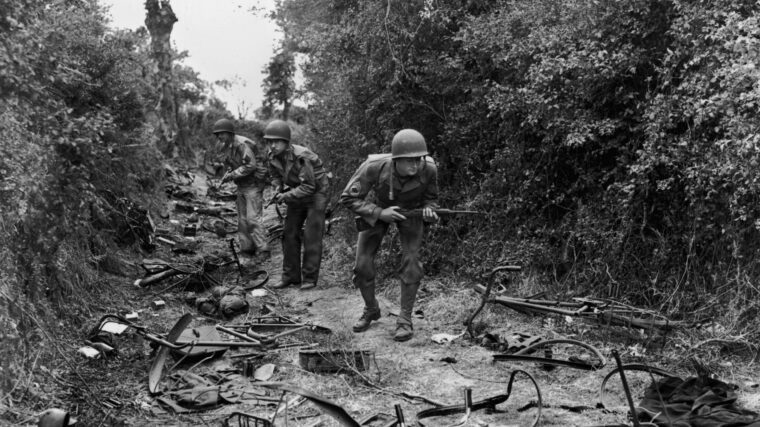

D-Day
It was the storm that forced the battle. On June 19, 1944, a massive gale hit the English Channel, sweeping in from the west, hitting the gigantic artificial harbors the Allies had built on their D-Day invasion beaches. Read more
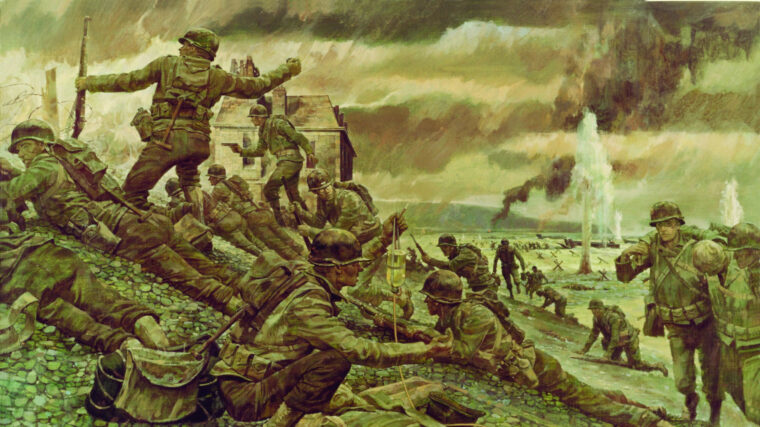

D-Day
The U.S. 29th Infantry Division was formed in July 1917, three months after America entered World War I. Read more
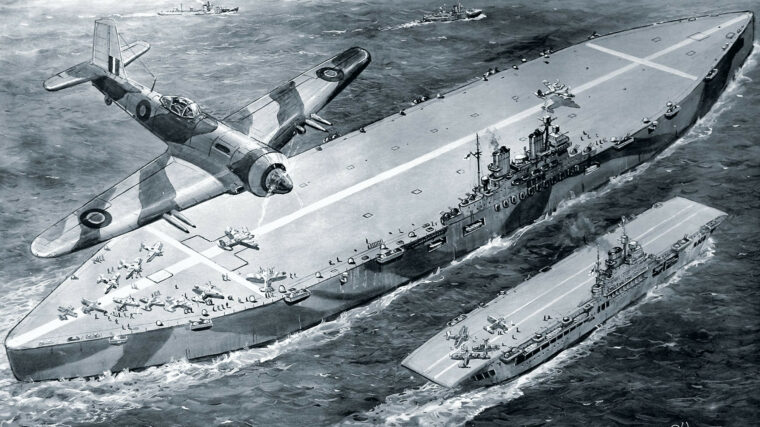
D-Day
During World War II British and American aircraft carriers, serviced and ready for naval combat, averaged 20,000 to 30,000 tons. Read more
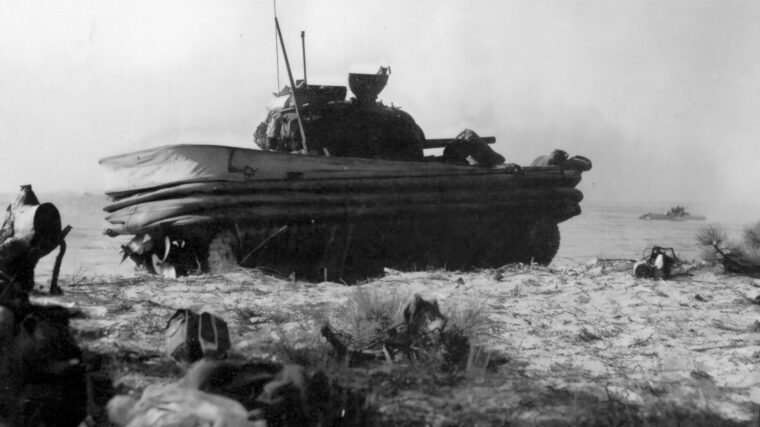

D-Day
German defenders hunkered in their concrete and steel bunkers along the Normandy coast were in for two major shocks on Tuesday, June 6, 1944. Read more

D-Day
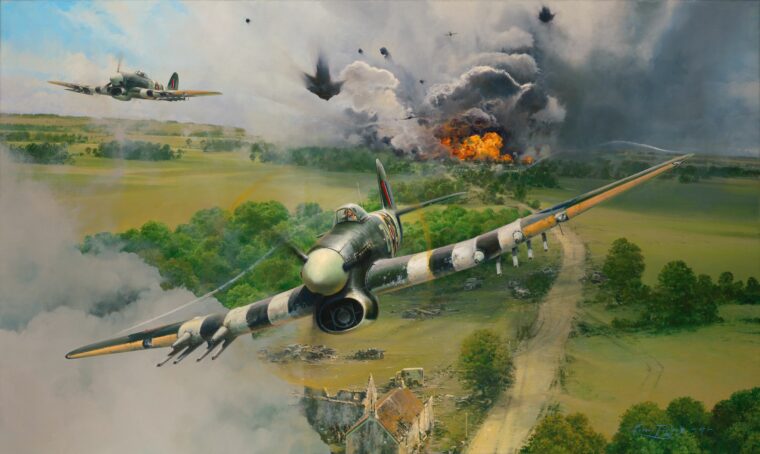
From the Supermarine Spitfire to the North American P-51 Mustang, and from the Soviet Yak series to the Vought F4U Corsair, the Allies were able to field a formidable array of fighter planes against the Axis powers in World War II. Read more

D-Day
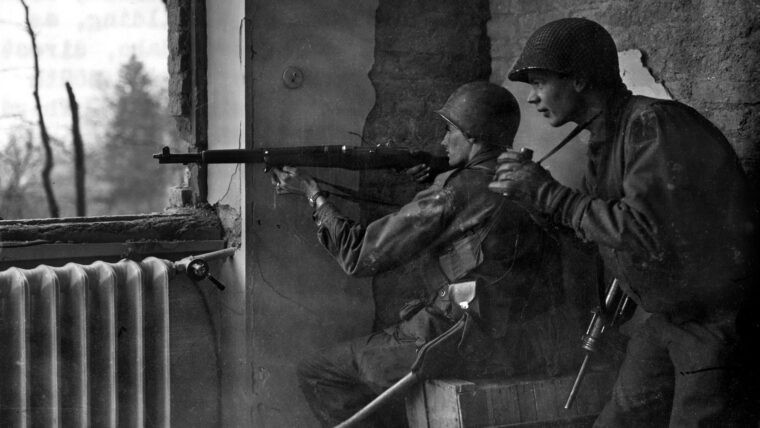
Lieutenant General Omar Bradley, commander of the U.S. First Army, considered his 90th Infantry Division a problem unit. Read more

D-Day
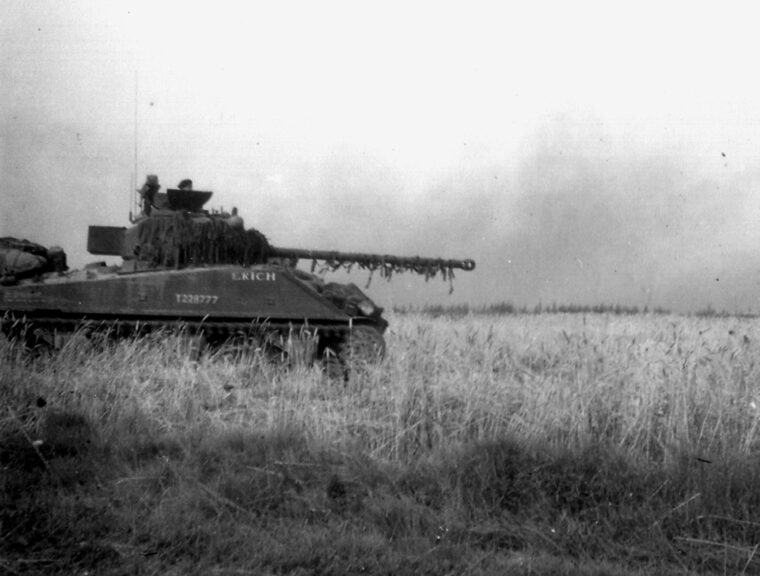
For the Allied tankers and infantrymen of the American, British, Canadian, and Free French armies battling German Panther and Tiger tanks in Normandy in the summer of 1944, the Sherman tank’s failures were glaringly evident as their own shells bounced off the hulls of the Nazi armor and they were themselves destroyed at a far greater range by the powerful German tanks. Read more

D-Day
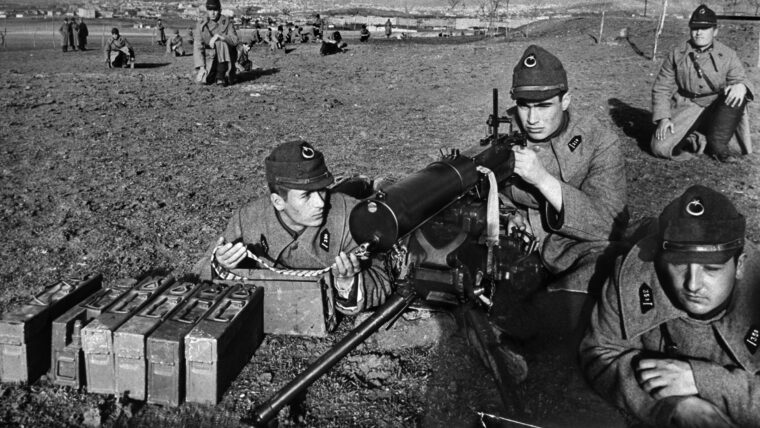
Maybe the Turks were just bad at picking the winning side. In World War I the Central Powers were defeated by the Allies, so in October 1939 they switched to ally with Britain and France. Read more