Pearl Harbor
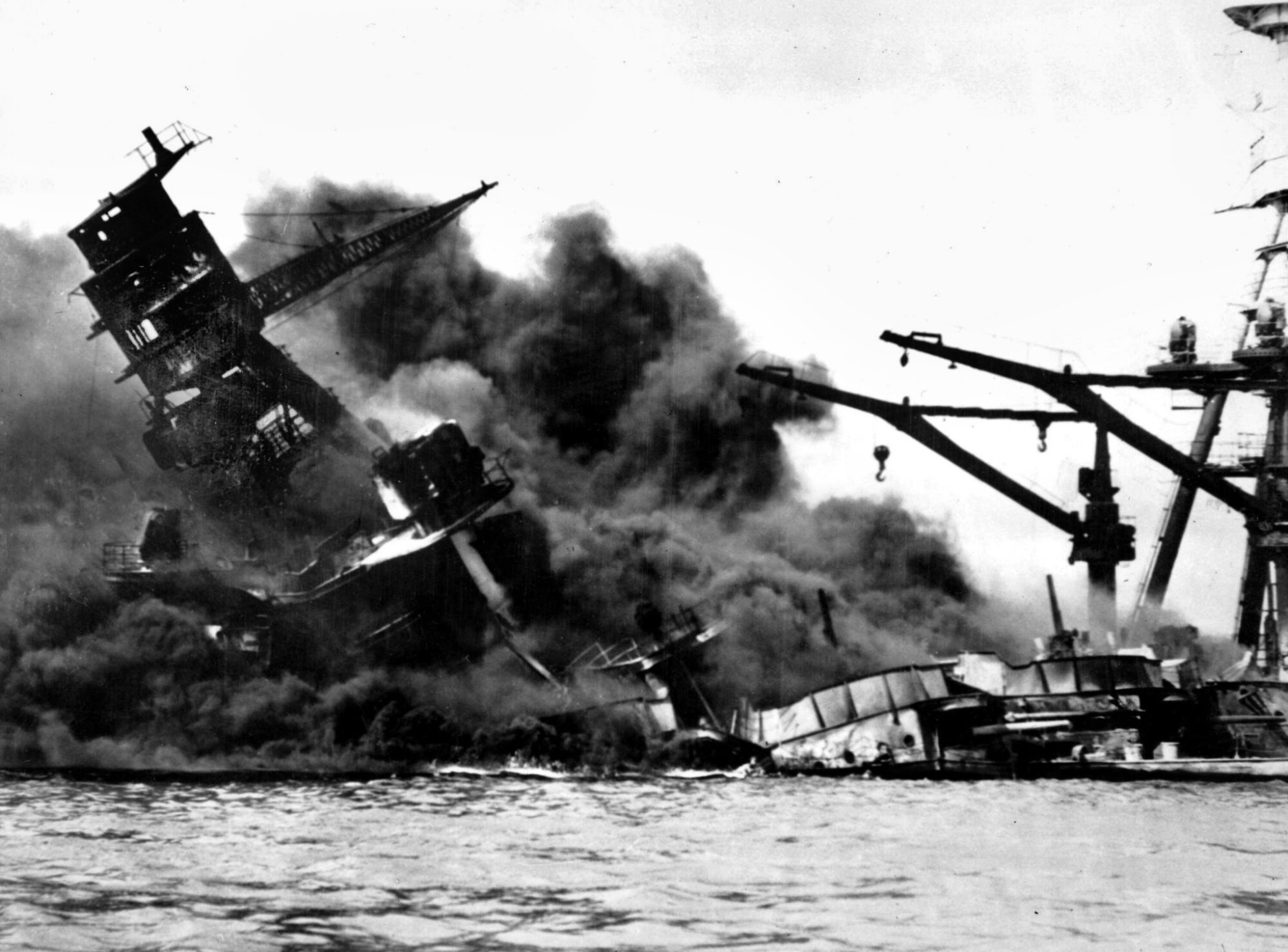
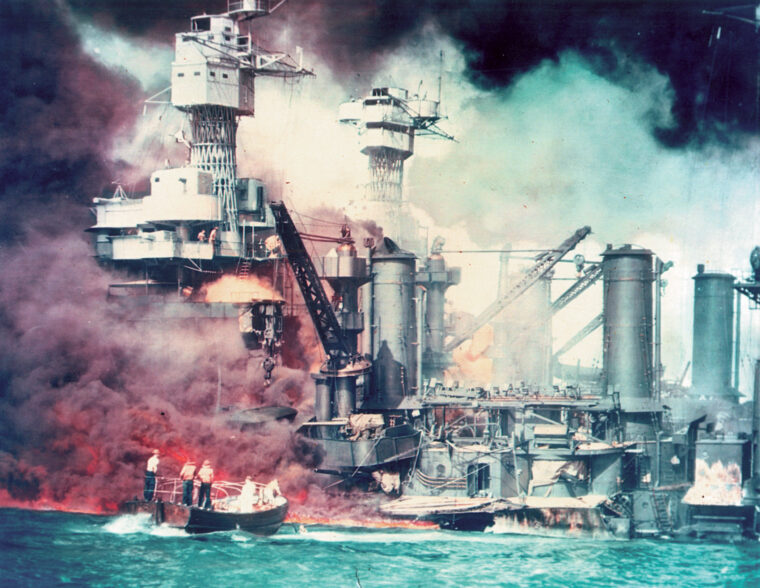
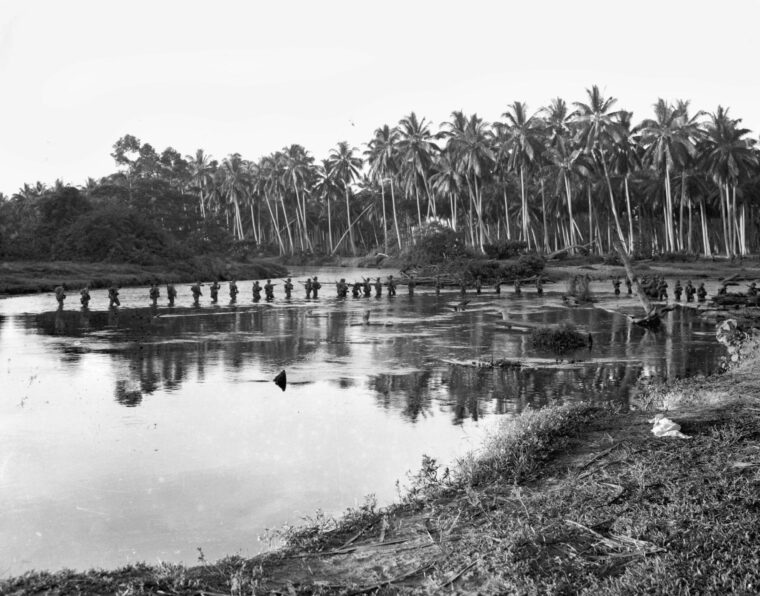
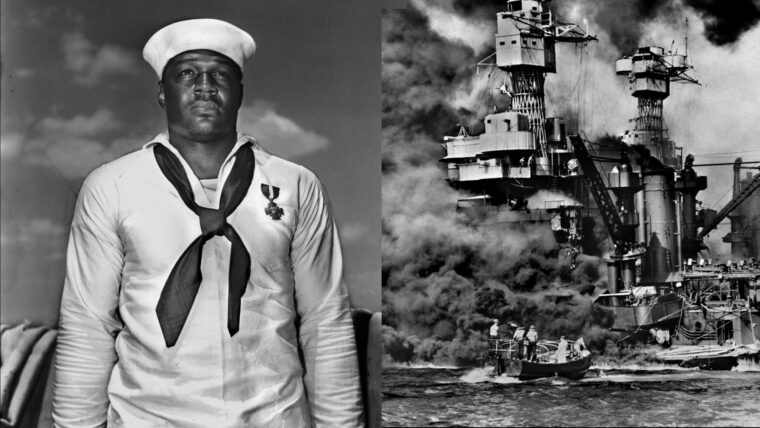
The attack on Pearl Harbor and other U.S. military installations on the island of Oahu, territory of Hawaii, Sunday, December 7, 1941, plunged the United States into World War II. The Pearl Harbor anchorage of the U.S. Navy’s Pacific Fleet was attacked by two waves of Japanese planes flying from aircraft carriers more than 200 miles north of Hawaii. Eight battleships of the Pacific Fleet, as well as numerous other ships, were sunk or damaged, and 2,403 American lives were lost. Pearl Harbor has become an enduring symbol of American resolve in the wake of the surprise air raid. President Franklin Roosevelt called the date of the Pearl Harbor attack one that would “live in infamy.”