By John W. Osborn, Jr.
“The first I saw of Madagascar and the last after adventurous months ashore was the eerie color of the soil,” a British novelist turned security sergeant would write a decade later.
“It gave to the sky, the vegetation, and the people a strangeness, even a deathliness which still shadows my recollections of the island. For the soil and the dust which rose from it to cake our skins and clothes, our eyelids and nostrils was not brick-colored or terra cotta but the color of dried blood.”
Lying 240 miles off the southeast coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, at 226,658 square miles Madagascar ranks just behind Greenland, New Guinea, and Borneo in size among the world’s islands. But with a population in 1942 of just 3.4 million, it had one of the world’s smallest densities, five persons per square mile. Only 25,000 were French, the rest a mixture of African with ancient arrivals from Malaya and Polynesia dizzyingly divided into 18 sub-ethnic groups such as the Antandroy, the “people of the bush brambles,” and the Tsmimihety, the “people who do not cut their hair.”
Though discovered by Europeans in 1506, its French rulers did not bother to take possession until 1897. Under the rule of Vichy collaborators, the island was ignored and isolated for most of the war; however, events in the Pacific brought it briefly into the action.
When he heard of the attack on Pearl Harbor in his London headquarters, the leader of the Free French, General Charles de Gaulle, asked an aide what he thought the consequences would be for France.
“The Indian Ocean becomes a major theater of operations, and Madagascar suddenly takes on strategic importance. The Japanese will try to seize it,” the aide astutely answered.
In Japanese hands, the magnificent harbor of Diego Suarez at the northeast tip of the island and the naval base a mile to the south at Antisare could choke off Allied supply lines to India and Egypt. De Gaulle appealed to the Allies to take Madagascar, but British Prime Minister Winston Churchill vetoed the idea. “Our hands are too full,” he cabled President Franklin D. Roosevelt, and told his chief of staff, “Madagascar must still have low priority.”
But then the Japanese captured Singapore and Burma. They landed on the Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal. With Ceylon threatened, the British war cabinet decided on July 12, 1942, to seize only Diego Suarez rather than all of Madagascar.
“The rest of the enormous island was of less strategic importance,” Churchill later explained. “With the memories of Dakar in our mind, we could not complicate the operation by admitting the Free French. The decision was taken for a purely British expedition.”
Churchill called the campaign for Madagascar “our first large-scale amphibious operation since the Dardanelles.” Operation Ironclad got underway just 12 nights later, winter clothing seen loaded amid rumors of a commando operation against occupied Norway. Rear Admiral Neville Syfret commanded the aircraft carriers Illustriousand Indomitable,the battleship Ramillies,a pair of cruisers, nine destroyers, six corvettes, and an equal number of minesweepers. Maj. Gen. Robert Sturges commanded 13,000 troops.
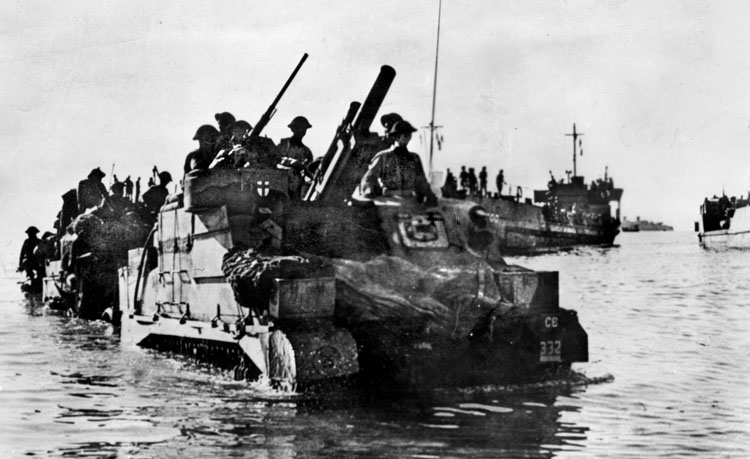

“It was the nearest I would come to realizing a conception of ‘adventure,’” Sergeant Rupert Croft-Cooke later wrote. He had already had his share of extraordinary experiences, working in a circus, traveling with a horse-drawn gypsy caravan, and wandering Europe in an old bus. The writer was now heading for the strangest of all.
The convoy rounded the Cape of Good Hope, spent five days docked in Durban, South Africa, to load supplies, then headed north into the Mozambique Channel separating Madagascar from the African mainland.
Facing the British would be 8,000 unenthusiastic local conscripts along with Foreign Legionnaires and tough Senegalese soldiers from West Africa. “We were told in a whisper that we had agents ashore keeping us informed of every defensive measure of the enemy,” Croft-Cooke wrote. The top British agent on Madagascar since November 1940 was Percy Mayer, a businessman whose work took him all over the island, while his wife, much admired in what passed for society with her looks and piano playing, tapped out his messages to Durban in their bathroom.
“But,” Croft-Cooke recalled, “when the last night came and we realized that in the small hours, the landing would start, the prospect, viewed in the tropical sunlight, suddenly seemed forlorn, uncertain of success, exceedingly dangerous.”
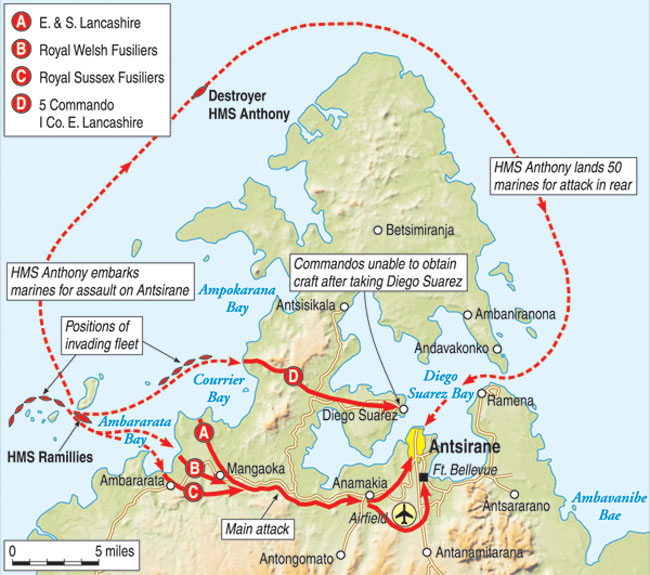
The campaign for Madagascar opened at 4:40 amon May 5, 1942, with the attack at Diego Suarez.
Fairey Swordfish and Albacore aircraft from the carriers bombed shipping at anchor in the harbor and destroyed most of Vichy’s 30 aircraft on the ground, while the fleet shelled the town and paratroopers descended.
Caught in town, Percy Mayer rushed from his hotel room into the street. Unluckily for him, he ran right into a Vichy patrol. When he was searched, secret messages were located on him. He quickly found himself in a cell at Antisare’s naval base, told he would be summarily executed, and was at least offered a priest.
Only the air strikes had been real. The naval bombardment had been star shells and signal rockets, light instead of heat, the “paratroopers” merely dummies. The real attack was taking place on the island’s western side, at Courier Bay and Ambarata.
“Firing at night is not to be contemplated, the entrance to the bay being considered impossible,” a French staff report confidently concluded. Royal Navy minesweepers were nonetheless able to skillfully navigate the shoals, reefs, and mines and then drop buoys for the troopships to follow.

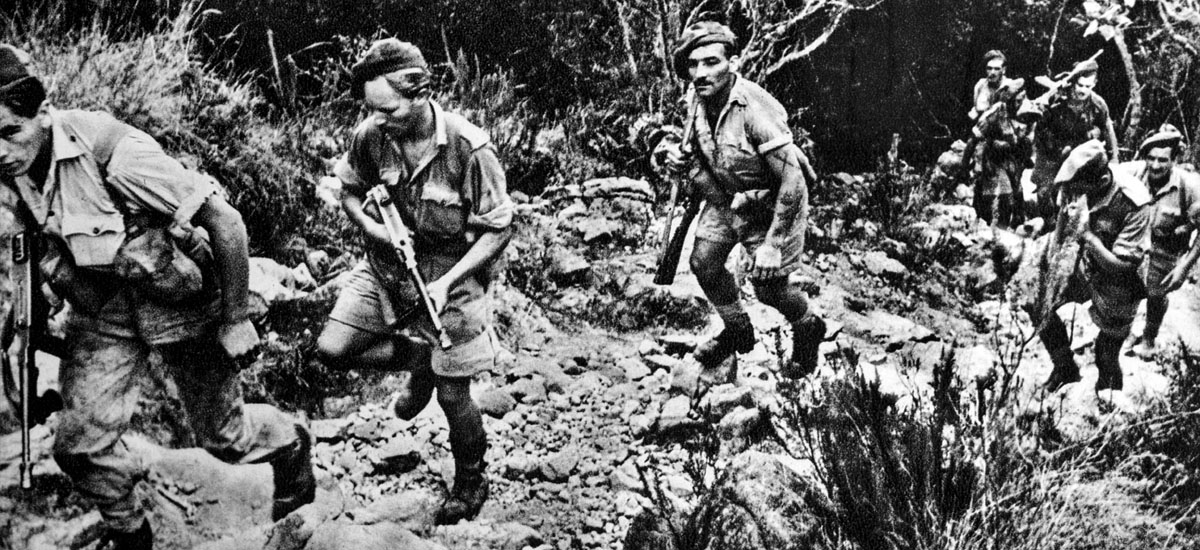
Commandos and East Lancashire regulars proceeded to scale the 50-foot cliff overlooking Courier Bay. “We moved up to a gun position which we could see clearly in the moonlight,” a Royal Artillery captain serving as a forward observer related. “Strangely enough, all was quiet and deserted, no sentries were posted, and no sign of life of at all. As dawn broke, we saw some buildings and went in to investigate. There we found the gunners all in bed.”
There was little initial opposition. “In sweltering heat, loaded like pack mules with ammo and grenades, we marched against a hot wind across the 8-mile isthmus to Diego Suarez,” one Commando remembered. When the Commandos and the Lancashire troops reached Diego Suarez at 4:30 pmthey finally met bitter resistance.
Sergeant Rupert Croft-Cooke and the 29th Independent Brigade, in the meantime, had come ashore at Ambarate. He dragged his motorcycle to shore, kicked it to life, then joined the advance up the single, dusty road 21 miles east toward Antisare. “There was no sound of firing, no glimpse of the enemy,” he wrote. “Ten miles or more distance were covered before we saw anything but red earth and florid vegetation.”
“Soon after noon, the battle started,” he continued. He had been traveling 20 yards behind the Bren carrier that the 29th’s commander, Brigadier Fredrick Festing, was riding in. Known as Frontline Frankie, he was, as usual, hundreds of yards ahead of the column when firing suddenly broke out. The British rushed to cover behind the roadside trees and bushes. After five minutes, one of a half-dozen supporting Valentine tanks clanked up. As he walked toward it, Festing saw Croft-Cooke and yelled, “Been fired on much, sergeant?”
“No sir, not at all.”
“I’ve got to speak to that tank,” Festing said and started whacking the turret with his walking stick. More irritated than impressed, Croft-Cooke rode back down the road to rejoin his security section.
Festing drove the Vichy defenders back with armor, then a bayonet charge. Hours later, descending a hill and coming to a bridge across a stream, the British vanguard came upon a dilapidated corrugated iron building with a sign that said “Robinson’s Hotel.”
It was actually a store. “In every village of Madagascar, we afterward learned, there was a Chinaman’s store, usually a tin shanty,” Croft-Cooke recalled. It was quickly taken over as field headquarters for Festing and Sturges, with Croft-Cooke in charge of the guard detail. All the while, the ancient Chinese proprietor served tea, chattering in his unique brand of French.
Three miles from Antisare, the surprised British ran into a network of pillboxes and trenches the Vichy soldiers called the Joffre Line. Percy Mayer, still sweating out his appointment with the firing squad, had reported on it, but the information had never reached Sturges.
“The firing was now intense and from all sides,” Croft-Cooke related. “Our own artillery and the French 75s were audible in the universal racket of mortars, machine-gun and rifle fire.” Festing threw in his armor, only to have it stopped by a 2,000-yard-long antitank ditch. The last four of the Valentines and two of the six light Tetrarch tanks making up the rest of the operation’s armor were knocked out by artillery fire. Their crews leaped out and fought Senegalese soldiers hand to hand to reach safety. Festing recommended Captain Peter Palmer, killed trying to save his wounded driver, for what would have produced the campaign’s only Victoria Cross, but he was instead awarded the Military Cross.
A long day came to a merciful end at 6:30 pm. “Now, it was deep night, and the crowded stars of the southern hemisphere shone brightly,” Croft-Cooke wrote. To prevent snipers from crawling up in the darkness, the British set the surrounding grass on fire. “I watched the blazing hills and the black shapes of our men against them, and tried to realize that this was a battle, and not merely a rather fantastic night in a strange country.”
Sturges prepared to launch a predawn attack, expecting “a good scrape which would end when we were at breakfast in Antisare.” Actually, he was having his breakfast at 7:30, still at Robinson’s. “It was quite clear that the attack had failed. It was an unhappy moment,” he admitted.
There were more unhappy moments to come. Despite the fires, snipers got through—a naval signalman sitting next to Croft-Cooke fell forward without a sound, a bullet between his eyes. Then, Robinson’s came under heavy artillery shelling, sending everyone but the Chinese owner dashing to cover. Sturges headed back to the coast to board Syfret’s flagship Ramilliesat 2 pm, “hot, begrimed, and unhappy,” in Syfret’s words, and requesting a diversionary seaborne raid against Antisare.
In less than 30 minutes, the destroyer Anthonywas setting out to race 100 miles around Madagascar with Captain Martin Price and 30 Royal Marines. One of them was Syfret’s valet, who begged to go, Syfret agreeing only with reluctance. He later admitted, “I did not expect a score to survive the night. The next hours were not happy ones.”
Lieutenant Commander John Hodges took the Anthonyinto Antisare Bay in pitch darkness at 8 pm, hoping to make a surprise landing, but searchlights on shore came on. Hodges steadily maneuvered through a gauntlet of fire at 30 knots toward the docks. With no time to stop, he overshot the dock, reversed in by the stern while Price and his Marines jumped off, and then headed full speed back out to sea.
Price divided his Marines to seize objectives. Those rushing the gate at the naval depot where Percy Mayer was taken for execution came under rifle fire. Grenades tossed in response soon had the commander emerging with a white flag. A bugler beside him started to sound the ceasefire. The Marines, mistaking it for an alarm, knocked him down and then apologized. Inside, 50 British prisoners taken in the morning’s failed assault on the Joffre Line were liberated, but not Percy Mayer. Luckily, he had not been shot: sensing defeat, the French had ostensibly paroled him.
Price armed the prisoners and soon had Antisare under control, and despite Syfret’s fears, he had not lost even a single Marine. “This was a brilliant diversion,” wrote Churchill. Price was awarded the Distinguished Service Order for it. Sturges ordered a final assault on the Joffre Line at 8:30. Phone calls from Antisare reported that Price’s raid had broken Vichy morale, and at 11 pm, the burst of signal rockets illuminated the black sky, announcing that the Joffre Line had fallen.
The last holdouts in Diego Suarez gave up in the morning. “It was as though we had won a hard game of rugger, and neither team appeared to have any ill feeling,” Price commented.
Rupert Croft-Cooke saw nothing sporting about the score in losses, for 105 British had been killed and 283 wounded, while Vichy French losses were 145 dead and 336 wounded. “There was little for triumph in our entry,” he wrote. “We were angry at the idiotic obstinacy of the French, who had fought and killed many a good fellow. And why? Because an octogenarian marechal at home had ordered them to do so.”
Another soldier was just as angry: Charles De Gaulle. He was in Washington, D.C., to mend relations with President Roosevelt when a reporter awakened him at midnight for a comment—the first word he had received of the invasion. For the moment, the British preferred to deal with the local Vichy authorities. They would find them as hard to handle as De Gaulle, but for a different reason.

When the police, customs officers, teachers, and other assorted necessary functionaries were summoned to the town hall in Diego Suarez and asked by the British to continue working, they protested, one of them asking how it would endanger their pensions to, ironically, collaborate with the occupiers.
The British made the gesture of threatening to jail them so they could claim later they served under duress. Croft-Cooke, for one, could not hide his disdain for such people “who, thinking that their pensions might be lost or their good name obscured in the eyes of their government, refused to admit the one consideration which should have counted with a Frenchman as it did with an Englishman: the defeat of the Boche who sprawled across France and of the Jap who occupied Indo-China.”
Croft-Cooke got on with his own security work, freeing imprisoned Gaullists, rounding up Vichy sympathizers for questioning, and starting a dogged pursuit of two German agents. He even governed for a while as an acting district officer. “I came to like the Malagasy, his innocent mendacity, his primitive timidity, his talent for storytelling, his indolence, courtesy, and sweetness,” he later wrote.
In the meantime, the British left the French in control of central and southern Madagascar, to his irritation. He wrote in 1953, “One day, I suppose, we shall be told why it was that having taken the only strongly defended port in Madagascar, we remained precariously within an area of 100 square miles before attacking and controlling the rest of the island.”
Three years before, Winston Churchill had explained why. In the fourth volume of his World War II history, The Hinge of Fate,he included a telegram to Admiral Syfret regarding Madagascar. “It must be a help and not a hindrance. It must be a security and not a burden. We cannot lock up field troops there for any length of time,” it read. Syfret had, in fact, concurred. “I think, as far as our occupation of Diego Suarez is concerned, the French will adopt a policy of live and let live.”
Before long, though, the Japanese again forced Churchill to change his mind, this time directly.
“We had settled down to life in that scruffy little seaport as though we would remain there forever,” wrote Croft-Cooke. On the night of May 29, 1942, sudden explosions in the harbor shattered that tranquility.
Ramillieshad a 20-foot hole blown it its side. An oil tanker was sunk. “Where had they come from? What did it portend?” worried Churchill.
It had been a Japanese midget submarine. Attempting to escape after doing the damage, it ran aground on a reef, the two crewmen swimming ashore to be cornered and killed two days later.
During the next two months, several more midget submarine attacks destroyed 34 ships totaling 150,000 tons. The (erroneous) assumption—the midgets actually launched from Japanese fleet submarines—was that the Japanese were operating from the ports still in Vichy hands: Majunga on the west coast, Tamatave on the east. The premier of South Africa, Jan Smuts, put particular political pressure on Churchill, cabling, “Madagascar is the key to the safety of the Indian Ocean. It all points to the necessity of eliminating Vichy control from the whole island as soon as possible.”
The British first responded with bombing missions into Vichy territory by the South African Air Force. One aircraft with a pilot named Jones went down, and Croft-Cooke was sent on a rescue mission to get him back. Jones, though, had salvaged a machine gun from his wrecked bomber and was leading his crew to safety when they were suddenly faced with a French officer and 40 men.

“I must ask you, gentlemen, to consider yourselves my prisoners,” said Jones, firing a burst from the machine gun into the air. The Malagasy accompanying the French officer scattered.
The Frenchman responded, “I surrender unconditionally.” With his prisoner in tow, Jones reached the coast to be picked up by the Royal Navy. Croft-Cooke also found the German agents he was hunting. After receiving a tip, he nabbed them before dawn while they were sleeping in a hut.
“The west coast ports were needed for control of the Mozambique Channel where our convoys were molested by the U-boats. The governor-general remained obdurate. Further operations had to take place,” wrote Churchill. In the end, the decision was finally made to occupy the remainder of Madagascar in a three-stage operation named Stream Line Jane.
Stream would be a landing at Majunga, followed immediately by Line, a march on Madagascar’s capital, Antananarivo, finishing with Jane, a landing at Tamatave. A convoy of reinforcements including the famed King’s African Rifles (KAR) sailed from Mombasa to rendezvous in the Mozambique Channel with Croft-Cooke and the 29th Brigade on the night of September 9, 1942.
Another writer, Kenneth C. Gandar-Dower, was with the reinforcing troops that night. He had flown a rickety two-seater from England to India, later exploring Kenya and the Belgian Congo and publishing accounts of his exploits. The war provided him more opportunity for exotic adventure as a correspondent covering first the invasion of Ethiopia and now Madagascar.
“The world was dark and empty for us—and Madagascar,” he wrote of that night at sea. “I did not know what lay ahead.” What did lie ahead was an episode that would go down in British lore as the Battle Before Breakfast.
The invasion force appeared off Majunga at 3 am. “Between the troopships, something was moving, a little black blob that seemed to have no shape,” Gandar-Dower wrote. “After a while, I realized it was not alone. There was another, and another, and another.”
They were assault craft carrying East Lancashire troops and Welsh Fusiliers to the beach nine miles out of town. When daylight came, his ship moved to 400 yards from shore, and he watched “little figures crawl slowly up cliffs of white chalk, following the convolutions of a winding track, halting, going on…. It was if we cut away half an ant hill, replaced by a pane of glass, and through the glass, were watching ants at war.”
In fact, he was watching a feint attack like the one at Diego Suarez.
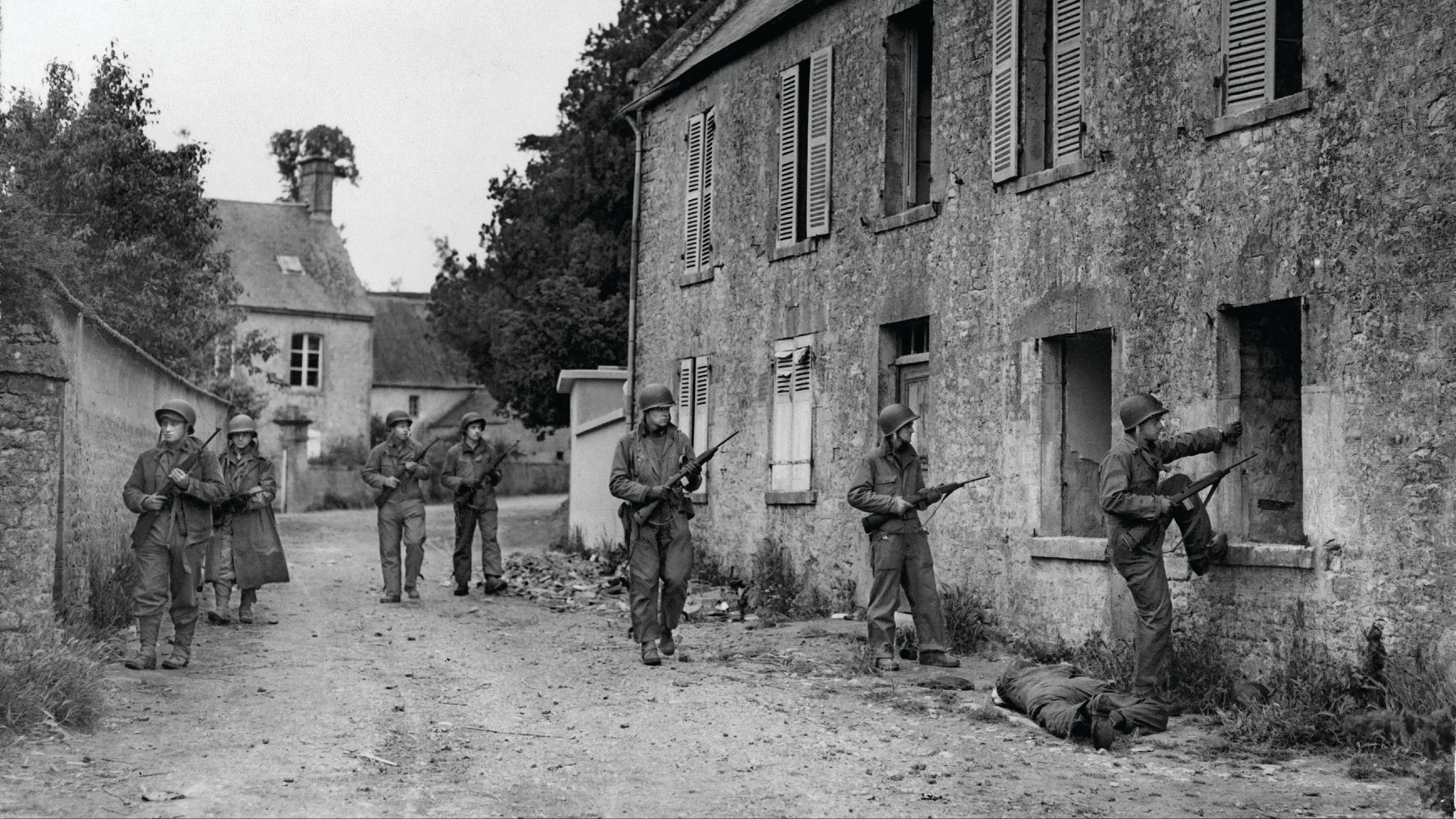
Croft-Cooke was coming in with the real landing force, headed straight for the docks. “It took an hour and a half to reach the shore,” he related, “and before we had done, dawn had arrived. We could see Majunga in the rosy light of sunrise, a white city among palms. At first, it seemed peaceful enough, but as we were within earshot, we could hear the sound of machine guns, and we knew the French were resisting. We caught a glimpse of the Commandos hurrying up a narrow street and saw our men along the white sand of the beach.”
The Commandos landed at 5:20, quickly overwhelmed the machine guns then swarmed into the town. Croft-Cooke followed, pushing his ever-present motorcycle through the surf and sand. “The fighting was almost over, but a few shots were still audible to give me the illusion of taking part in a fight for the town,” he recalled.
The Commandos met only scattered resistance as they occupied the bank, post office, and residence of the regional administrator, and in 90 minutes, the battle—such as it was—ended with a dozen British dead. Commandos trying to flank the town had run into a far different, more determined opponent.
“As we traveled up the river,” Fred Munson remembered, “the tide began to go out, and we began to run aground on a sandbank. The river was full of crocodiles, so before we could get into the water to lighten the craft and push them off the sandbanks, hand grenades were thrown into the river to keep the crocodiles at bay.”
In Majunga, the garrison commander, Major Didier Martins, got caught in bed at the time of the attack but managed to get himself slightly wounded in the left elbow and, no doubt for the benefit of his Vichy superiors, made a show of presenting himself with a theatrically oversized sling.
“Did my men fight well?” he asked.
“Magnificently!” the British commander played along.
As at Antisare, finding a bugle to call surrender proved difficult. A young British officer was sent to the Martins home for a white flag. He found Madame Martins hysterically barricaded in her bedroom.
From outside the door, the officer explained why he was there and assured her that he was not going to rape her. The door finally creaked open, and a trembling hand passed out a broomstick and bed sheet. “A curious gaiety spread through the town at lunchtime,” Croft-Cooke observed. “We were openly welcomed, and the hope was expressed we should occupy the capital before long.”
By then, the KAR and a South African armored car column had set out 250 miles southeast to do just that. They covered 131 miles in just 18 hours, only to be slowed to a crawl by the first of some 3,000 roadblocks Vichy forces were eventually to put up all over Madagascar. The KAR worked around the clock dismantling the obstacles and met their only serious opposition 150 miles from Atananarivo, at the mountain village of Ariba.
Senegalese troops kept the KAR under heavy machine-gun fire until a sergeant named Odillo, whose British officer had been killed, led his platoon around the Senegalese and then came screaming down on them wielding three-foot-long, curved panga machetes.
“After firing to the last, one of the Senegalese would jump out and try to scuttle through our lines. We dropped a number of them like rabbits,” the KAR colonel said. Four of the KAR died in the fight, while the eight wounded were laid without rancor or bitterness alongside Senegalese casualties, though neither would accept being put next to a Malagasy conscript.

After 13 days, the column reached Atananarivo to be met by a Special Operations Executive operative, Royal Navy Lieutenant Peter Simpson Jones, standing by a Renault in a crisp, new tropical suit. He and a companion had delivered a radio set to another agent, but their dinghy had capsized in Madagascar’s notoriously shark-infested waters while they were rowing out for pickup. The companion drowned, but Jones was rescued by a fisherman. At his court-martial, at which he was sentenced to five years in prison, the Vichy prosecutor had suggested, “Don’t you think in the next world war,you might do better to join the artillery?”
Percy Mayer’s piano-playing, radio key-tapping wife, who spent several anxious weeks expecting arrest, was also safe. Governor General Armand Annet had fled, and with no one to take the surrender, a British officer walked into the radio station to politely request airtime for a not quite historic announcement:
“At 5 pm, our troops occupied Atananrivo. Everything is quiet. That is all.”
Five days earlier, the Jane portion of the operation had taken place. With the surf at Tamatave too rough for landings in the dark, the plan was to intimidate the town into surrender with an overwhelming show of naval force. “They might bluff up to the last minute, but not beyond it. The guns would never have to fire,” Gandar-Dower believed, but he was proven wrong—for three minutes.
That was how long the British bombardment went on after the French had rejected a 10 AM ultimatum. They hoisted a white flag at 10:03. Gandar-Dower sloshed ashore, bowler hat on head, camera in one hand, typewriter in the other, to witness a great deal of activity—soldiers in firing positions, rushing about, kicking in doors–but no action. “It was,” he wrote, “like a Hollywood assault, which was being held up by the failure of the other side to put in an appearance.”
An old woman shuffled up to him to ask if the battle was over. It was, he said, and soon he and the British were marching into town, at their head, a young lady “in the shortest of bathing costumes and pair of first-class legs.”
Even though Stream Line Jane had been successfully completed, the campaign for Madagascar would drag on for six senseless weeks. With a mix of defiance and delusion, Governor General Annet had sent off a crazed cable to Vichy: “Our available troops are preparing to resist every enemy advance with the same spirit which inspired our soldiers at Diego Suarez, at Majunga, at Atananarivo, where each time the defense became a page of heroism written by La France.”

He had fled 190 miles south to Finanarantsoa, and the KAR had set off in pursuit. Gandar-Dower followed in a confiscated Citroen truck, bicycle, and pirogue, admitting, “We saw little of the war, but met with a great deal of curious adventure.”
Rupert Croft-Cooke was having his own adventure with a lieutenant and a half-dozen soldiers searching for a French lieutenant with 100 conscripts. Along the way, they had encountered crocodiles, chasing them off with rifle shots. They later came upon a female English missionary, alone, forgotten, and resigned to staying after over 40 years.
“Five hours of being paddled up a crocodile-infested river in Madagascar to a collection of native huts does not prepare one for such an encounter,” Croft-Cooke wrote. Then he and the lieutenant finally had their discussion with the French officer:
“You have, of course, some soldiers?” the Frenchman asked.
“Yes,” the British one replied. “We have some soldiers.”
“Naturally, they are armed?”
“Naturally.”
“Automatic weapons, I presume?”
“Tommy guns.”
“You have, perhaps, some other forces in the area?”
“We have.”
“With some artillery, no doubt?”
“Certainly.” It was back at the coast.
“Ah. You will excuse me a moment.” He immediately wired Annet, “Occupied today by British forces armed with automatic weapons and supported by artillery.”
The campaign became one more of annoyance than action as the stubborn Vichy put up hundreds more roadblocks. “When I shut my eyes and think of Madagascar, I see one enormous roadblock,” Gandar-Dower remembered.
The French laid melon-sized rocks exactly 20 yards apart for miles and erected 18-foot stone walls. In the last significant action, the KAR turned an attempted ambush on itself, marching 30 miles around to attack from the rear, killing 40 and taking 800 prisoners. The Malagasy, always quick to run from battle, were now running away for good, deserting in droves. Even worse for the Vichy, law and order were breaking down. Croft-Cooke was an official witness at the execution by firing squad of a Malagasy for the unprecedented murder of a French settler.
After a five-week march, the KAR reached Finanarantsoa, only to find that Annet had fled another 190 miles southwest. With the KAR still in pursuit and after almost being killed when his staff car was strafed from the air, Annet finally sent his aide, Captain Louis Fauche, to negotiate surrender. In a 650-mile march, the KAR had routed 6,000 defenders for a loss of five British officers killed, six wounded and 20 Africans killed, 76 wounded.
Fauche agreed to surrender with the curious condition that it did not go into effect for another 10 hours, until 12:01 amon November 6, 1942.
The reason turned out to be, to the very end, about career concerns. Having the campaign last for exactly six months qualified the French for medals, promotions, and even cash awards, but any chance was dashed days later. To cap the fruitless futility of it all in Madagascar, the Germans occupied Vichy France.
Churchill was modestly satisfied with the campaign for Madagascar. “We had gained full military control over an island of high strategic importance to the safety of our communication with the Near and Far East,” he noted. “The Madagascar episode was in its secrecy of planning and tactical execution a model of amphibious operations. The news arrived at a time when we sorely needed success. It was in fact for long months the only sign of good and efficient war direction of which the British public were conscious.”
De Gaulle was angered at being left out. Kenneth Gandar-Dower, by contrast, later wrote, “It was for me a fascinating experience, an isolated six weeks of strange adventure.” He admitted that it was “certainly more than an exercise, but very much less than a war…. The French consciously or unconsciously conducted their defense according to formula. The first was ‘maximum results for minimum expenditure.’ The second: ‘resist as long and as fiercely as you can without loss of life—either French or British.’” Gandar-Dower’s exotic adventuring and writing ended when his transport was torpedoed en route to Ceylon on February 12, 1944.
Rupert Croft-Cooke soon left Madagascar for his next and last wartime posting, India. He spent most of his postwar life in other out-of-the-way locales, including Morocco and Tunisia, after serving six months in prison for homosexual activity in England in 1953, but he was through with Madagascar. He later wrote, “I shall never go back to Madagascar with its blood-red earth and creeping shadows.”
He continued with his prolific, if ultimately forgotten, writing and in 1953 published his account of events in Madagascar titled The Blood-Red Island. Tragically, Madagascar would become that, and not just from the soil. An uprising in 1947 against the French was crushed with perhaps 100,000 dead, and independence in 1958 was marked by more violence and tribal strife.
Author John W. Osborn, Jr., is resident of Laguna Niguel, California. He has written for WWII History on a variety of topics.








