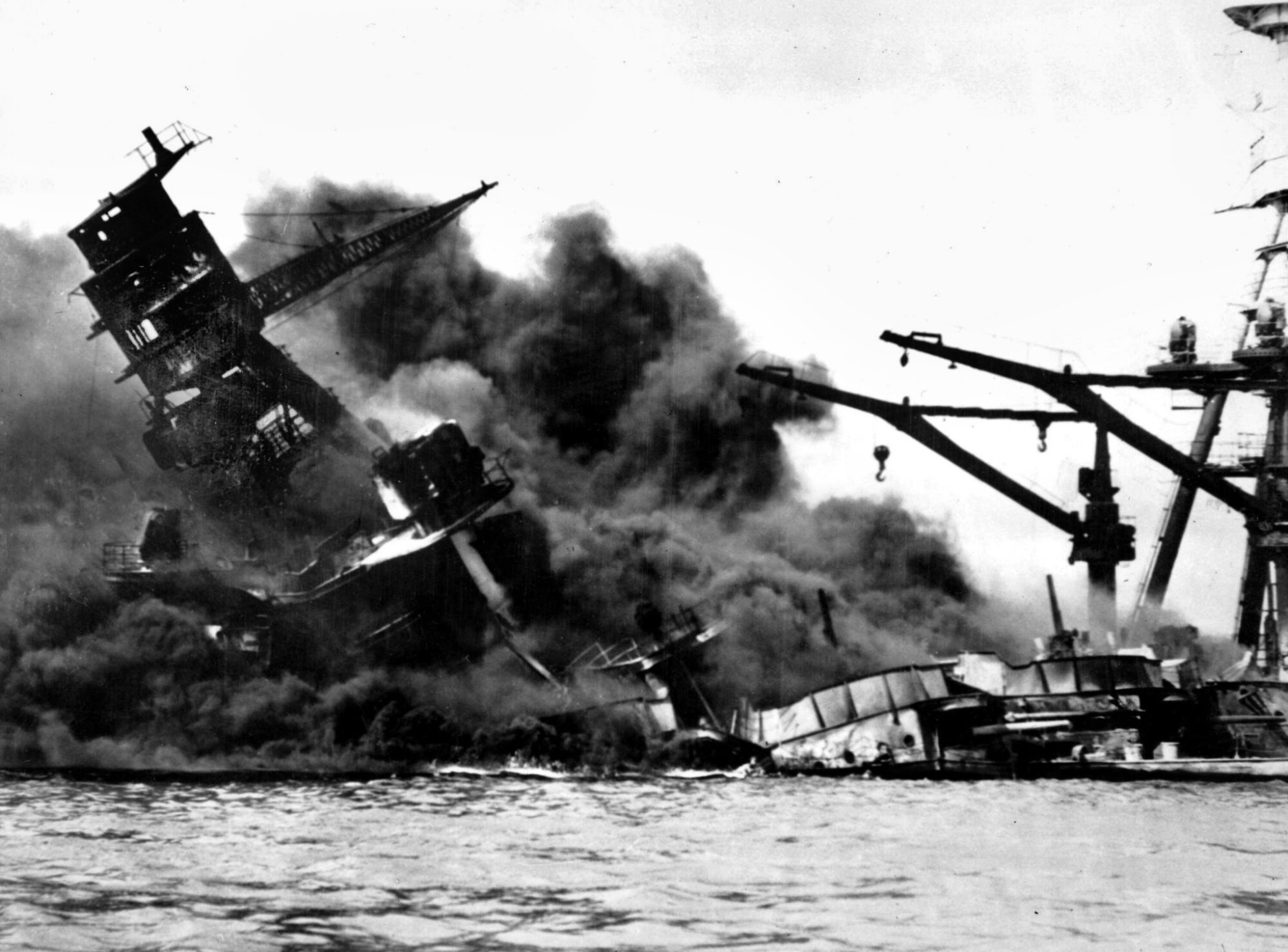
Pearl Harbor
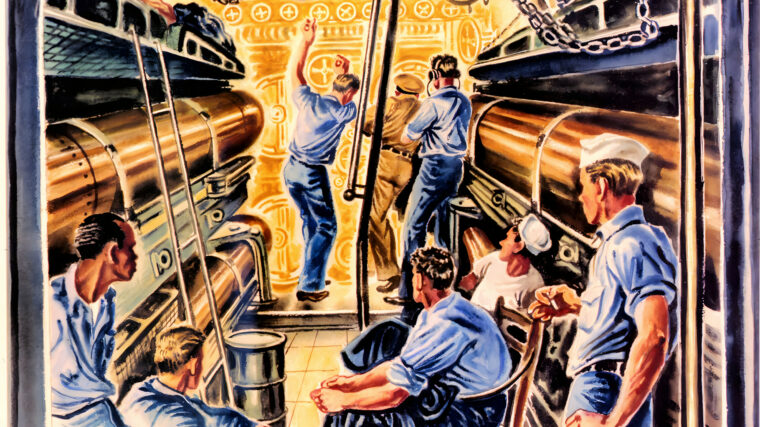
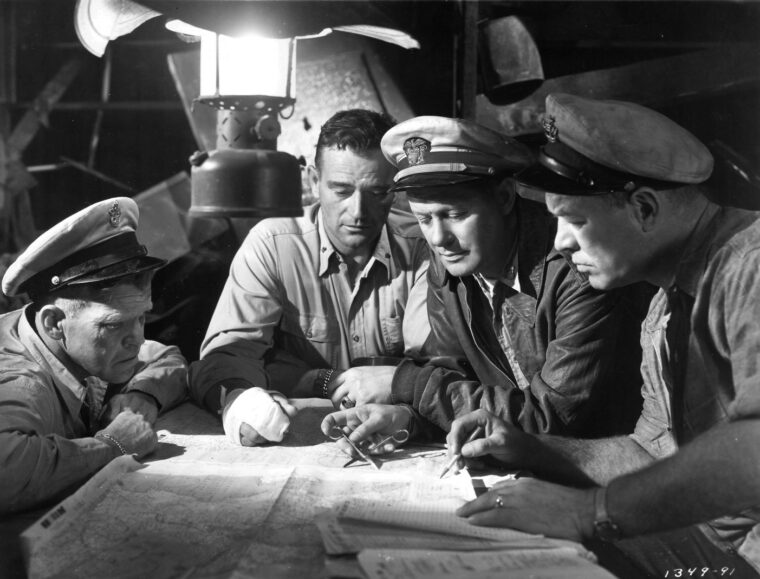
The Silent Service: A Submariner Aboard the USS Seal
By Ron SmithBACKSTORY: In World War II, the American submarine force was inordinately small—just 252 total boats, compared to the more than 1,100 deployed by Germany and over 600 built by Japan. Read more